Accurate measurement of paint and coating fineness—or grinding fineness—is critical for product quality, affecting color uniformity, gloss, durability, and storage stability. Traditionally assessed manually via ISO 1524:2013, this method suffers from human error such as inconsistent scraping speed, lighting conditions, and observation angles. These variables can dramatically distort measurement outcomes. By contrast, automated systems standardize the procedure through mechanized scraping, camera imaging, and software analysis—significantly reducing variability.
Fineness determines how finely pigment particles are dispersed. Finer dispersion leads to less inter-pigment space, resulting in smoother film, richer color, better gloss, and lower risk of pigment agglomeration. These properties are essential for ensuring product performance and consistency.
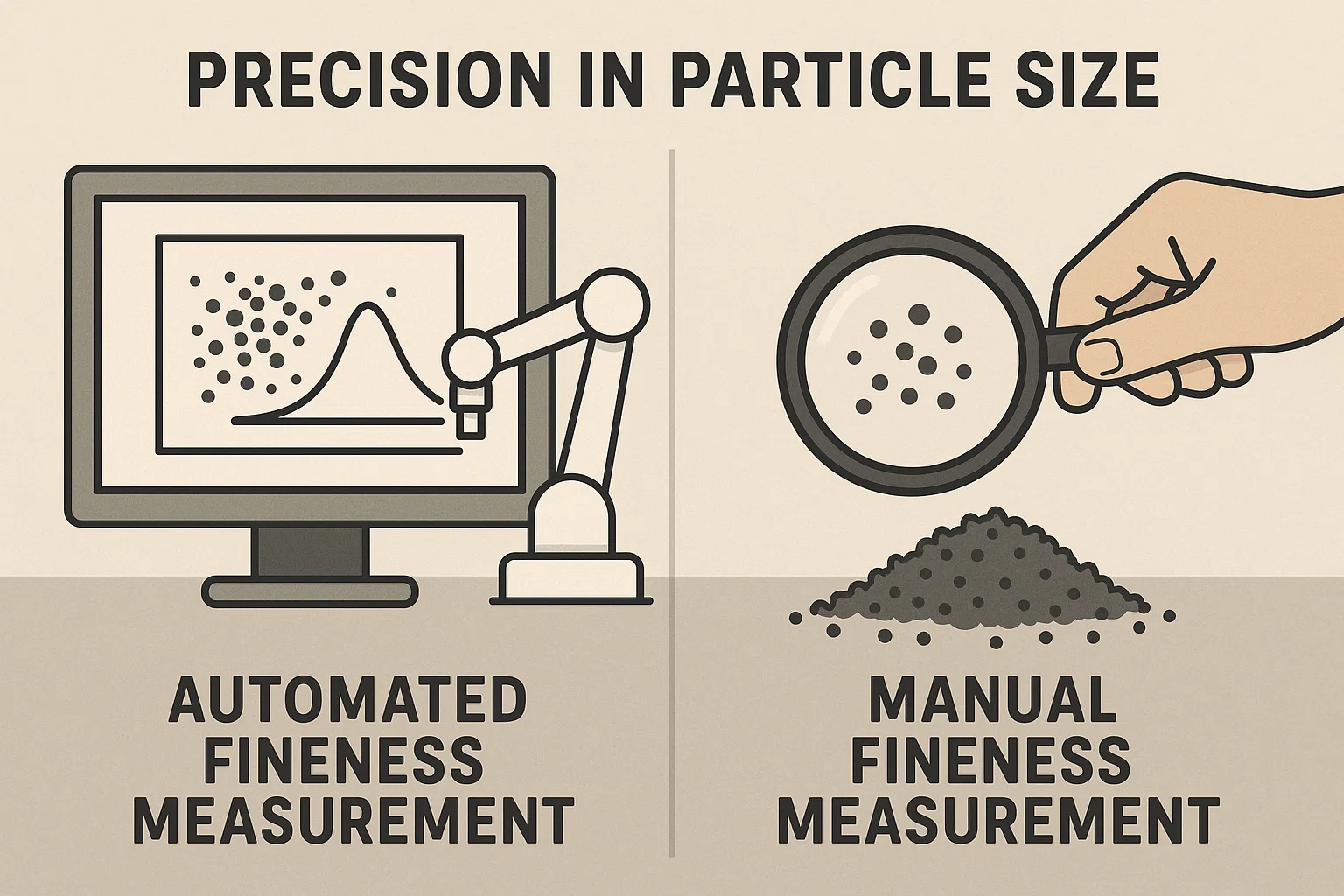
Manual fineness measurement involves a technician dragging a bar across a coating sample on a precision plate, then using a microscope or magnified visual reading. Factors that can introduce variability include:
These human-dependent variables often lead to significant result variance, especially with coatings that harden quickly. Moreover, the method demands skilled operators and frequent calibration to produce reliable results.
Automatic fineness meters mechanize the scraping and combine it with real-time visual capture and software analysis. Benefits include:
This automation addresses critical weaknesses of manual testing, delivering reliable results with less operator dependency and higher throughput.
The study controlled variables while measuring white latex paint fineness via both manual and automatic methods. The manual results fluctuated widely due to multiple factors, whereas automatic testing remained stable. Below is a summary of influential factors affecting manual testing:
List of Influencing Factors (Manual Method):
Each of these can skew the fineness value. Automatic meters minimize or fully eliminate these influences by standardizing the measurement environment.
For testing labs and production lines:
However, labs should validate automated systems against existing benchmarks and configure lighting and camera settings for their specific paint formulations.
Contact: [email protected] | +86 15773162403 | www.zpigments.com